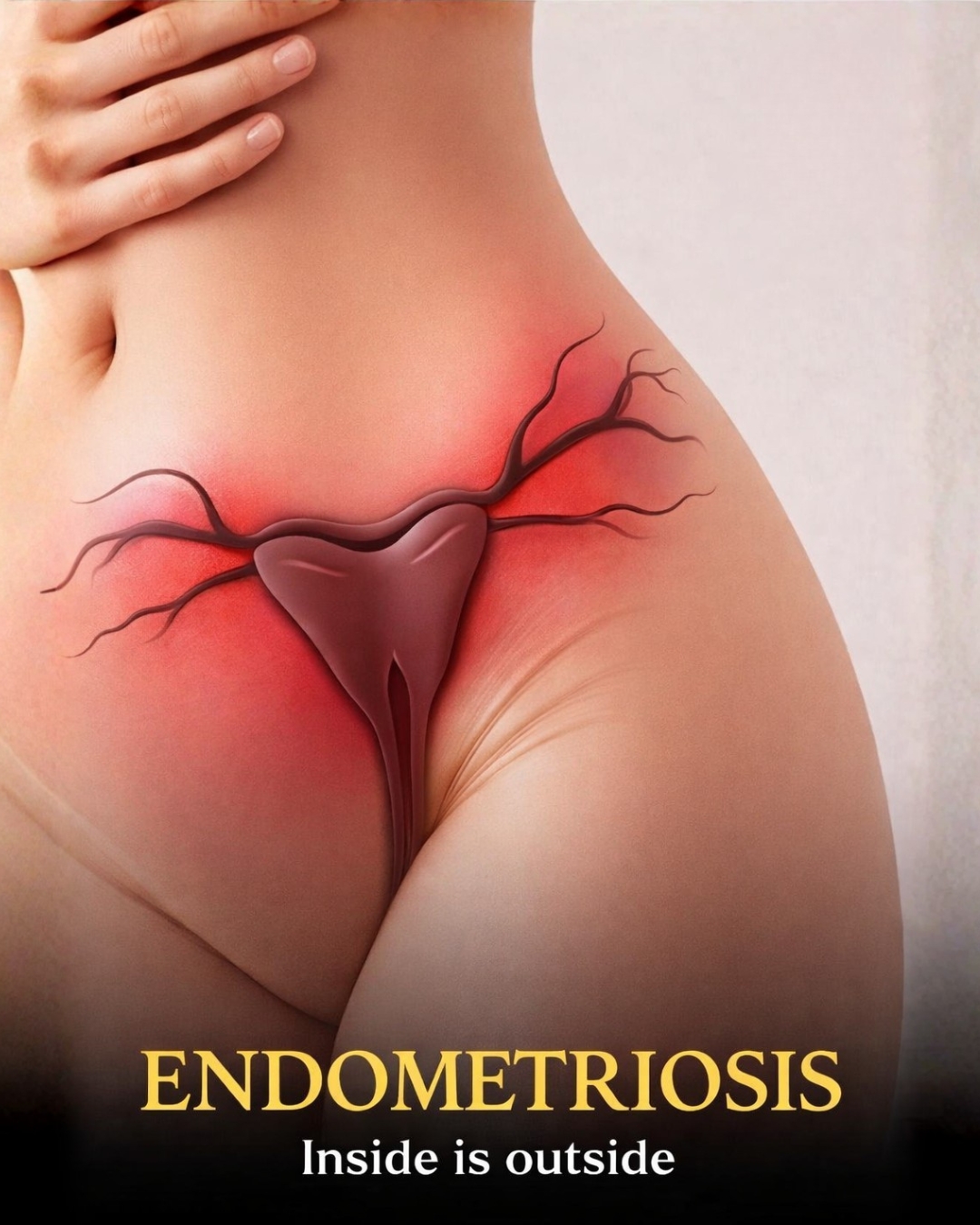
Have you ever heard of endometriosis?
It’s a condition that affects millions of women worldwide, yet many continue to suffer in silence. Lack of awareness, delayed diagnosis, and stigma often make the journey harder than it should be. Understanding endometriosis is the first step toward better health, early intervention, and improved quality of life.
This article breaks down what endometriosis really is, why it matters, and how it can be managed.
What Is Endometriosis?
Endometriosis is a chronic health condition in which tissue similar to the lining inside the uterus (the endometrium) grows outside the uterus.
This tissue can be found on the ovaries, fallopian tubes, pelvic lining, and sometimes even beyond the pelvic area.
Just like normal uterine lining, this tissue:
-
Thickens
-
Breaks down
-
Bleeds during each menstrual cycle
The problem is that this blood and tissue have no way to exit the body, causing inflammation, irritation, and scar tissue. Over time, this leads to pain and other serious complications.
Common Symptoms of Endometriosis
Pain is the most noticeable and defining symptom, but endometriosis can affect each woman differently.
Common signs include:
-
Severe menstrual cramps that may start before your period and last several days
-
Chronic pelvic or lower back pain
-
Pain during or after sex
-
Heavy menstrual bleeding or bleeding between periods
-
Difficulty getting pregnant
-
Digestive issues such as bloating or constipation during periods
-
Fatigue and low energy levels around menstruation
Because symptoms can overlap with other conditions, many women go undiagnosed for years.
What Causes Endometriosis?
The exact cause is still unclear, but researchers believe several factors may play a role:
-
Retrograde menstruation: Menstrual blood flows backward into the pelvic cavity instead of leaving the body
-
Genetic factors: Having a mother or sister with endometriosis increases risk
-
Immune system dysfunction: The body may fail to recognize and eliminate misplaced tissue
-
Hormonal influence: Estrogen appears to fuel the growth of endometrial-like tissue
Endometriosis is not caused by lifestyle choices, and it is not something you can “prevent” on your own.
How Is Endometriosis Diagnosed?
Diagnosis can be challenging because symptoms often mimic other conditions such as pelvic inflammatory disease (PID) or irritable bowel syndrome (IBS).
Doctors typically use a combination of:
-
Detailed medical and family history
-
Pelvic examinations
-
Imaging tests such as ultrasound or MRI
In some cases, surgery may be needed to confirm the diagnosis.
Endometriosis and Fertility
Endometriosis is one of the leading causes of infertility.
-
Over 30% of women with endometriosis experience difficulty getting pregnant
-
Scar tissue and adhesions can block fallopian tubes
-
Inflammation can interfere with egg fertilization and implantation
The good news is that many women with endometriosis still conceive naturally or with medical support and go on to have healthy pregnancies.
Management and Treatment Options
There is currently no cure, but symptoms can be managed effectively.
Common treatment approaches include:
-
Over-the-counter pain relievers for mild discomfort
-
Prescription pain medications for severe pain
-
Hormonal therapies to reduce or stop menstruation
-
Surgery in severe cases to remove endometriosis tissue
-
Lifestyle changes such as regular exercise, stress management, and adequate sleep
Treatment is highly individual and should always be guided by a healthcare professional.
The Role of Diet in Endometriosis
Diet may influence symptoms, although research is still ongoing.
Some evidence suggests:
-
Eating fewer fatty foods may help lower estrogen levels
-
High-fiber foods may support hormone balance
-
Diets rich in plant-based foods may reduce inflammation
-
High consumption of red meat has been linked to increased risk
While diet alone cannot cure endometriosis, mindful nutrition may help ease symptoms and support overall health.
Living With Endometriosis
Endometriosis is a long-term condition that can impact work, relationships, mental health, and self-confidence. Managing it requires patience, support, and proper care.
Seeking help from healthcare providers, connecting with support groups, and leaning on loved ones can make a significant difference. No one should feel alone in this journey.
Raising awareness helps reduce stigma, encourages earlier diagnosis, and empowers women to advocate for their health. ❤️
Sharing knowledge can change lives.